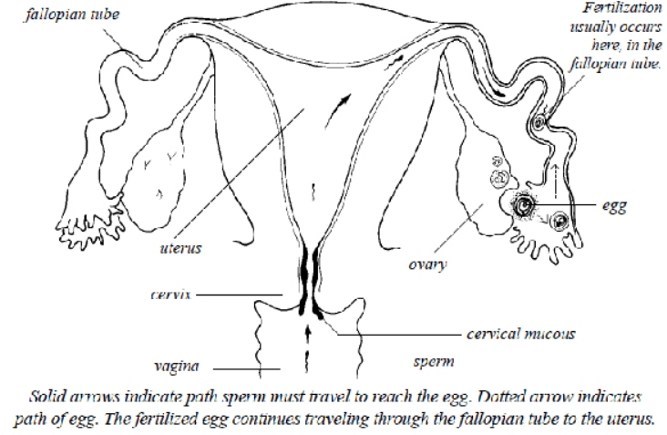
In a normal pregnancy, an ovary releases an egg into the Fallopian Tube (fallopian tubes on either side of the Uterus connect the ovaries to the Uterus) where it meets with a sperm that fertilizes the egg, following which the fertilized egg travels to the Uterus and attaches itself to the Uterine lining for nine months. On the other hand, when the Fallopian tubes prevents the sperm from reaching the ovary to fertilize an egg or prevents a fertilized embryo from reaching the Uterus for pregnancy, then you’re suffering from a condition called Tubal factor infertility.
The most common causes of Tubal factor infertility include:
A Tubal blockage is identified in the following cases:
Patients have a high risk of tubal factor infertility if they’ve had a ruptured appendix or previous abdominal surgeries, including surgeries for ectopic pregnancies, a condition in which the embryo grows outside of the uterus. Due to the location of these conditions, tubal issues are more likely to occur.

Symptoms include:
Diagnosis includes:
There are two main treatments for Tubal Factor Infertility, one is surgical and the other is non-surgical. In case the two fail, then there is IVF that can used to achieve pregnancy.
Ways to repair a tube include:
Before going ahead with the decision, the advantages and disadvantages of IVF and tubal surgery should be reviewed with the patient to arrive at the appropriate choice.
Coming to IVF, its main advantages of IVF are good per-cycle success rates and it is less surgically invasive. On the other hand, its disadvantages include cost (especially if more than one cycle is required) and the need for frequent hormone injections and monitoring for several weeks.
Likewise with Tubal surgery, there is the risk of scar tissue and adhesions and also the chance of recurrent blocked tubes after surgery, pelvic infection or an ectopic pregnancy. However, the chances of conceiving naturally after surgery is greater if the patient is young and has a minimal amount of scar tissue blocking the fallopian tubes.
Further, certain patient factors also need to be taken into consideration like:
In addition, other factors that need to be taken into consideration include patient’s preference, patient’s religious beliefs and the cost and insurance of the treatment procedure.
To decide between the two, if it comes to that, a semen analysis can be performed in the infertility investigation, as these results may influence the decision between tubal surgery and IVF.
It’s an operation to help find out why the woman is having difficulty becoming pregnant. The dye test will expose as to whether the fallopian tubes are blocked or not. Likewise Laparoscopy helps to find out whether if the woman has Endometriosis, pelvic infection, adhesions, ovarian cysts or fibroids.
A laparoscopy and dye test helps to find out the cause of infertility, particularly if the fallopian tubes are blocked. Some minor treatments can be performed at the same time.
A laparoscopy and dye test can help the doctor at JFC find out the cause of your infertility.
Under a Laparoscopy and Dye test (usually performed under a general anesthesia), the Gynecologist will
The whole of the surgical operation usually takes about fifteen minutes.
Coming to recovery part, the patient would be able to go home the same day or the day after. Before that, a member of the team at JFC will tell you about the results of the laparoscopy and dye test and then discuss the possibilities of any treatment or follow-up to be taken.